The old version is still available here
Monitor HTML5 video element
This guide walks through integration with any HTML5 video player to collect video performance metrics with Mux data. Use this if Mux does not have an SDK specific for your player.
In this guide:
Features
Features
The features supported by Mux Data for this player.
1
Install mux-embed
Install mux-embed
Install mux-embed either from our CDN or from the npm registry.
2
Initialize Mux Data
Initialize Mux Data
Attach mux-embed to your player so that Mux can collect playback metrics.
3
Make your data actionable
Make your data actionable
Use metadata fields to make the data collected by Mux actionable and useful.
4
Changing the video
Changing the video
If your implementation changes the video without changing the video player, let mux-embed know to start tracking a new view.
5
Advanced options
Advanced options
Depending on the details of your implementation, you may want to leverage some of the advanced options of mux-embed.
Release notes
Release notes
Features
The following data can be collected by the Mux Data SDK when you use the HTML Video Element SDK, as described below.
Supported Features:
- Engagement metrics
- Quality of Experience Metrics
- Web metrics such as Player Startup Time, Page Load Time, etc
- Available for deployment from a package manager
- Custom Dimensions
- Custom Beacon Domain
Live Latency is available for Native Safari HLS.
1Install mux-embed
Include the Mux JavaScript SDK on every page of your web app that includes video. You can use the Mux-hosted version of the script or install via npm. mux-embed follows semantic versioning and the API will not change between major releases.
If possible, use the SDK for your particular player (e.g. Video.js, JW Player, etc.). While the HTML5 SDK works with any modern HTML5 video player, the player-specific Mux SDK is preferable because it offers a deeper integration and in most cases collects more pieces of data. If you don't see your player listed then use mux-embed and let us know so we can prioritize creating an SDK for the player that you are using.
npm install --save mux-embed2Initialize Mux Data
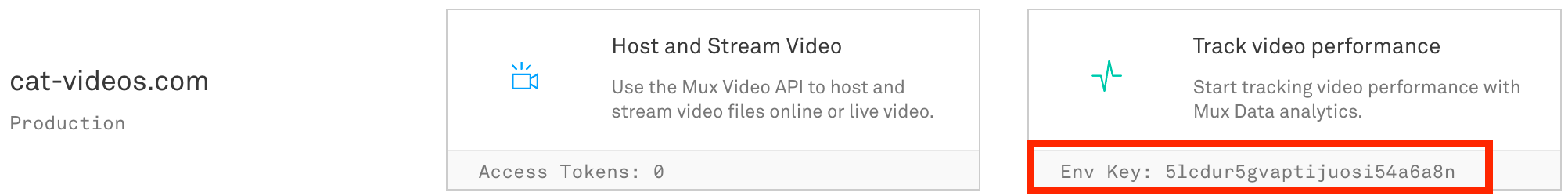
Get your ENV_KEY from the Mux environments dashboard.
Env Key is different than your API token
ENV_KEY is a client-side key used for Mux Data monitoring. These are not to be confused with API tokens which are created in the admin settings dashboard and meant to access the Mux API from a trusted server.
import mux from 'mux-embed';
const playerInitTime = mux.utils.now();
// Initialize Mux Data monitoring by passing in the "id" attribute of your video player
mux.monitor('#my-player', {
debug: false,
data: {
env_key: 'ENV_KEY', // required
// Metadata fields
player_name: 'Main Player', // any arbitrary string you want to use to identify this player
player_init_time: playerInitTime,
// ...
}
});Call mux.monitor and pass in a valid CSS selector or the video element itself. Followed by the SDK options and metadata. If you use a CSS selector that matches multiple elements, the first matching element in the document will be used.
Log in to the Mux dashboard and find the environment that corresponds to your env_key and look for video views. It takes about a minute or two from tracking a view for it to show up on the Metrics tab.
If you aren't seeing data, check to see if you have an ad blocker, tracking blocker or some kind of network firewall that prevents your player from sending requests to Mux Data servers.
3Make your data actionable
The only required field in the options that you pass into mux-embed is env_key. But without some metadata the metrics in your dashboard will lack the necessary information to take meaningful actions. Metadata allows you to search and filter on important fields in order to diagnose issues and optimize the playback experience for your end users.
Pass in metadata under the data key when calling mux.monitor.
mux.monitor('#my-player', {
debug: false,
data: {
env_key: 'ENV_KEY', // required
// Site Metadata
viewer_user_id: '', // ex: '12345'
experiment_name: '', // ex: 'player_test_A'
sub_property_id: '', // ex: 'cus-1'
// Player Metadata
player_name: '', // ex: 'My Main Player'
player_version: '', // ex: '1.0.0'
player_init_time: '', // ex: 1451606400000
// Video Metadata
video_id: '', // ex: 'abcd123'
video_title: '', // ex: 'My Great Video'
video_series: '', // ex: 'Weekly Great Videos'
video_duration: '', // in milliseconds, ex: 120000
video_stream_type: '', // 'live' or 'on-demand'
video_cdn: '' // ex: 'Fastly', 'Akamai'
}
});For more information, view Make your data actionable.
4Changing the video
There are two cases where the underlying tracking of the video view need to be reset:
- New source: When you load a new source URL into an existing player.
- New program: When the program within a singular stream changes (such as a program change within a continuous live stream).
Note: You do not need to change the video info when changing to a different source of the same video content (e.g. different resolution or video format).
New source
If your application plays multiple videos back-to-back in the same video player, you need to signal when a new video starts to the Mux SDK. Examples of when this is needed are:
- The player advances to the next video in a playlist
- The user selects a different video to play
See metadata in Make your data actionable for the full list of video details you can provide. You can include any metadata when changing the video but you should only need to update the values that start with video_.
It's best to change the video info immediately after telling the player which new source to play.
const myPlayer = document.querySelector('#my-player');
myPlayer.src = 'https://muxed.s3.amazonaws.com/leds.mp4';
mux.emit('#my-player', 'videochange', {
video_id: 'abc345',
video_title: 'My Other Great Video',
video_series: 'Weekly Great Videos',
// ...
});New Program
In some cases, you may have the program change within a stream, and you may want to track each program as a view on its own. An example of this is a live stream that streams multiple programs back to back, with no interruptions.
In this case, you emit a programchange event, including the updated metadata for the new program within the continuous stream. This will remove all previous video data and reset all metrics for the video view, creating a new video view. See Metadata for the list of video details you can provide. You can include any metadata when changing the video but you should only need to update the values that start with video.
Note: The programchange event is intended to be used only while the player is currently not paused. If you emit this event while the player is paused, the resulting view will not track video startup time correctly, and may also have incorrect watch time. Do not emit this event while the player is paused.
mux.emit('#my-player', 'programchange', {
video_id: 'abc345',
video_title: 'My Other Great Video',
video_series: 'Weekly Great Videos',
// ...
});5Advanced options
Disable cookies
By default, Mux plugins for HTML5-based players use a cookie to track playback across subsequent page views. This cookie includes information about the tracking of the viewer, such as an anonymized viewer ID that Mux generates for each user. None of this information is personally-identifiable, but you can disable the use of this cookie if desired. For instance, if your site or application is targeted towards children under 13, you should disable the use of cookies.
This is done by setting disableCookies: true in the options.
mux.monitor('#my-player', {
debug: false,
disableCookies: true,
data: {
env_key: 'ENV_KEY',
// ... rest of metadata
}
}Over-ride 'do not track' behavior
By default, mux-embed does not respect Do Not Track when set within browsers. This can be enabled in the options passed to Mux, via a setting named respectDoNotTrack. The default for this is false. If you would like to change this behavior, pass respectDoNotTrack: true.
mux.monitor('#my-player', {
debug: false,
respectDoNotTrack: true, // Disable tracking of browsers where Do Not Track is enabled
data: {
env_key: 'EXAMPLE_ENV_KEY',
// ... rest of metadata
}
}Customize error tracking behavior
Errors are fatal
Errors tracked by mux are considered fatal meaning that they are the result of playback failures. If errors are non-fatal they should not be captured.
By default, mux-embed will track errors emitted from the video element as fatal errors. If a fatal error happens outside of the context of the player, you can emit a custom error to the mux monitor.
mux.emit('#my-player', 'error', {
player_error_code: 100,
player_error_message: 'Description of error',
player_error_context: 'Additional context for the error'
});When triggering an error event, it is important to provide values for player_error_code and player_error_message. The player_error_message should provide a generalized description of the error as it happened. The player_error_code must be an integer, and should provide a category of the error. If the errors match up with the HTML Media Element Error, you can use the same codes as the corresponding HTML errors. However, for custom errors, you should choose a number greater than or equal to 100.
In general you should not send a distinct code for each possible error message, but rather group similar errors under the same code. For instance, if your library has two different conditions for network errors, both should have the same player_error_code but different messages.
The error message and code are combined together and aggregated with all errors that occur in your environment in order to find the most common errors that occur. To make error aggregation as useful as possible, these values should be general enough to provide useful information but not specific to each individual error (such as stack trace).
You can use player_error_context to provide instance-specific information derived from the error such as stack trace or segment-ids where an error occurred. This value is not aggregated with other errors and can be used to provide detailed information. Note: Please do not include any personally identifiable information from the viewer in this data.
Error translator
If your player emits error events that are not fatal to playback or the errors are unclear and/or do not have helpful information in the default error message and codes you might find it helpful to use an error translator or disable automatic error tracking all together.
function errorTranslator (error) {
return {
player_error_code: translateCode(error.player_error_code),
player_error_message: translateMessage(error.player_error_message),
player_error_context: translateContext(error.player_error_context)
};
}
mux.monitor('#my-player', {
debug: false,
errorTranslator: errorTranslator,
data: {
env_key: 'ENV_KEY', // required
// ... additional metadata
}
});If you return false from your errorTranslator function then the error will not be tracked. Do this for non-fatal errors that you want to ignore. If your errorTranslator function itself raises an error, then it will be silenced and the player's original error will be used.
Disable automatic error tracking
In the case that you want full control over what errors are counted as fatal or not, you may want to consider turning off Mux's automatic error tracking completely. This can be done by passing automaticErrorTracking: false in the configuration object.
mux.monitor('#my-player', {
debug: false,
automaticErrorTracking: false,
data: {
env_key: 'ENV_KEY', // required
// ... additional metadata
}Release notes
Current release
v4.18.0
- Add audio, subtitle, and encryption key request failures for HLS.js
- Capture ad metadata for Video.js IMA
- Capture detailed information from HLS.js for fatal errors in the Error Context
Previous releases
v4.17.0
- Extend
errorTranslatorto work withplayer_error_context
v4.16.0
- Add new
renditionchangefields to Shaka SDK - Adds support for new and updated fields:
renditionchange, error, DRM type, dropped frames, and new custom fields - Add frame drops to Shaka SDK
- Add new
renditionchangeinfo to Web SDKs - Adds the new Media Collection Enhancement fields
v4.15.0
-
update
mux.utils.nowto usenavigationStartfor timing reference -
fix issue where views after
videochangemight incorrectly accumulate rebuffering duration -
Resolved issue sending beacons when view is ended
-
Record
request_urlandrequest_idwith network events
v4.14.0
- Tracking FPS changes if specified in Manifest
v4.13.4
- Resolved issue sending beacons when paused
v4.13.3
- Fixed issue with monitoring network events for hls.js monitor
v4.13.2
- Fix an issue with sending unnecessary heartbeat events on the window
visibilitychangeevent
v4.13.1
- Fixes an issue with accessing the global object
v4.13.0
-
Collect the
x-request-idheader from segment responses to make it easier to correlate client requests to other logs -
Upgraded internal webpack version
-
Flush events on window
visibilitychangeevent
v4.12.1
- Use Fetch API for sending beacons
v4.12.0
- Generate a new unique view if the player monitor has not received any events for over an hour.
v4.11.0
- Detect fullscreen and player language
v4.10.0
- Replace query string dependency to reduce package size
- Remove
ImageBeaconfallback, removing support for IE9
v4.9.4
- Generate all
view_id's internally
v4.9.3
- Use common function for generating short IDs
v4.9.2
- Fixed an issue around the
disablePlayheadRebufferTrackingoption
v4.9.1
- Fix issue where
getStartDatedoes not always return a date object
v4.9.0
-
Support PDT and player_live_edge_program_time for Native Safari
-
Set a max payload size in mux-embed
v4.8.0
-
Add option
disablePlayheadRebufferTrackingto allow players to disable automatic rebuffering metrics. Players can emit their ownrebufferstartorrebufferendevents and track rebuffering metrics. -
Fix an issue with removing
player_error_codeandplayer_error_messagewhen the error code is1. Also stops emittingMEDIA_ERR_ABORTEDas errors. -
Now leaving Player Software Version for HTML5 Video Element unset rather than "No Versions" as it is no longer needed.
v4.7.0
- Add an option to specify beaconCollectionDomain for Data custom domains
v4.6.2
- Fix an issue with emitting heartbeat events while the player is not playing
v4.6.1
- Fix an issue with removing event listeners from window after the player monitor destroy event
v4.6.0
- Update hls.js monitor to record session data with fields prefixed as
io.litix.data. - Update the manifest parser to parse HLS session data tags
v4.5.0
- Add short codes to support internal video experiments
- Collect request header prefixed with
x-litix-* - Capture fatal hls.js errors
- Make
envKeyan optional parameter
v4.4.4
- Add a player events enum on the
muxobject (e.g.mux.events.PLAY) - Use the browser
visibilitychangelistener instead ofunloadto handle destructuring the player monitor.
v4.4.3
- Fix: Specify
video_source_is_livefor HLS.js monitor
v4.4.2
- Group events into 10 second batches before sending a beacon
v4.4.1
- Exclude latency metrics from beacons if
video_source_is_liveis nottrue
v4.4.0
- Add a lightweight HLS manifest parser to capture latency metrics for player's that don't expose an API for accessing the manifest.
- Allow players to emit
player_program_timeinstead of calculating internally
v4.3.0
- Add support for calculating latency metrics when streaming using HLS
v4.2.5
- Remove default
video_idwhen not specified by the developer.
v4.2.4
- Add minified keys for latency metrics
v4.2.3
- Add minified keys for new program time metrics
v4.2.2
- Fix bug causing missing bitrate metrics using HLS.js >v1.0.0
v4.2.1
- (video element monitor) Fix an issue where some non-fatal errors thrown by the video were tracked as playback failures
v4.2.0
- Fix an issue where views triggered by
programchangemay not report metrics correctly - Fix an issue where calling
el.mux.destroy()multiple times in a row raised an exception
v4.1.1
- Fix an issue where
player_remote_playedwasn't functioning correctly
v4.1.0
- Add support for custom dimensions
v4.0.1
- Support HLS.js v1.0.0
v4.0.0
- Enable sending optional ad quartile events through.
- Move device detection server-side, improving data accuracy and reducing client SDK size.
- Fix an issue where jank may be experienced in some web applications when the SDK is loaded.
v3.4.0
- Setting to disable rebuffer tracking
disableRebufferTrackingthat defaults tofalse.
v3.3.0
- Adds
viewer_connection_typedetection.
v3.2.0
- Adds support for
renditionchange.
v3.1.0
- Add checks for window being undefined and expose a way for SDKs to pass in platform information. This work is necessary for compatibility with react-native-video.
v3.0.0
- Setting to disable Mux Data collection when Do Not Track is present now defaults to off
- Do not submit the source URL when a video is served using the data: protocol
v2.10.0
- Use Performance Timing API, when available, for view event timestamps
v2.9.1
- Fix an issue with server side rendering
v2.9.0
- Support for Dash.js v3
v2.8.0
- Submit Player Instance Id as a unique identifier
v2.7.3
- Fixed a bug when using
mux.monitorwith Hls.js or Dash.js the source hostname was not being properly collected.